
Discard blocking solution, replace with antibody solution and incubate. Rinse the membrane, transfer to a container with blocking solution and incubate. Following incubation, perform a low-stringency wash followed by a high-stringency wash to refine the DNA. Remove the pre-hybridization solution and incubate the blot with the probe (incubation times will vary depending on the application). Prepare the probe mixture (a complementary DNA strand) and buffer. Remove the blot from the cross-linker, add the pre-hybridization solution and incubate. Prepare the pre-hybridization solution and add sample DNA. Blocking reduces non-specific binding to the membrane. When transfer is complete, cross-link DNA in a cross-linker, then rinse the membrane. Assemble the transfer apparatus with the membrane, Whatman paper, and gel and transfer in SSC or SSPE buffer. During the previous step, begin to prepare Whatman paper and nylon membrane for the transfer. Rinse with water, then wash with neutralization solution. Place the gel in a container with denaturing solution, and wash twice for 15 minutes on a shaker. Load samples into wells and include a DNA molecular weight marker. Gel electrophoresis: prepare an agarose gel and either TAE or TBE buffer (buffer selection will depend on the duration of the run and the size of the DNA fragments). Restriction digestion: digest the DNA with a restriction enzyme, and if necessary, concentrate digested DNA. Detection methods differ based on the probe label radiolabeled probes are visualized with X-ray film or phosphorimaging, and enzymatically labeled probes are visualized with chemiluminescent substrate. The fully hybridized labeled probe molecules will remain bound to the blot. Hybridization of complementary sequences occurs during incubation, and the unhybridized probe is removed by washing with buffer. The membrane is incubated with a nucleic acid probe that has a sequence homologous to the target sequence and is labeled with radioactivity, fluorescent dye, or an enzyme capable of generating a chemiluminescent signal. Following electrophoresis, the DNA on the gel is transferred to a nylon membrane. Smaller fragments will migrate farther on the gel than larger ones. The fragments are separated by size on an agarose or polyacrylamide gel via electrophoresis. The southern blot protocol begins with DNA extraction from the cells or tissues, which is then enzymatically digested to produce DNA fragments. Southern blots are used to determine the identity, size, and abundance of specific DNA sequences. Blotting techniques are selected based on the target molecule: DNA, RNA, or protein. This enables radiolabeled or enzymatically labeled antibody or DNA probes to bind the immobilized target, and the molecules of interest may then be visualized with various methods. 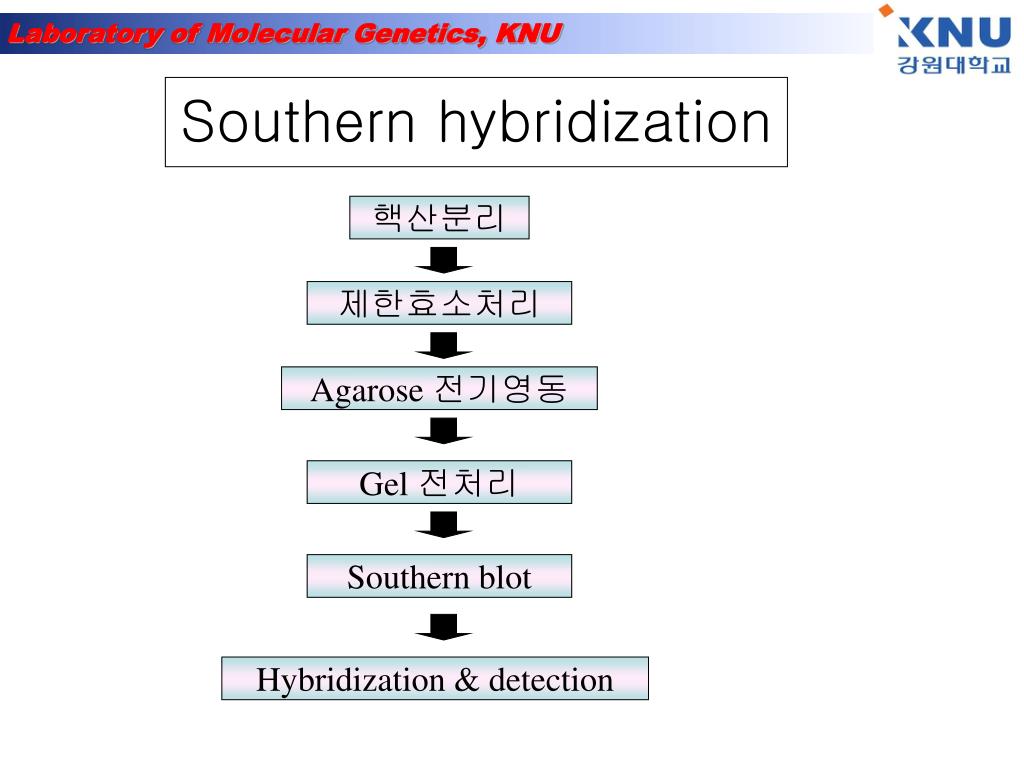
Southern, northern, and western blot protocols are similar, and begin with electrophoretic separation of protein and nucleic acid fragments on a gel, which are then transferred to a membrane (nitrocellulose membrane, polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane, etc.) where they are immobilized.
SOUTHERN HYBRIDIZATION ANALYSIS PDF
PDF Version What’s the difference between a Southern, Northern, and Western Blot?ĭifferent blotting techniques are used to identify unique proteins and nucleic acid sequences.





 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
